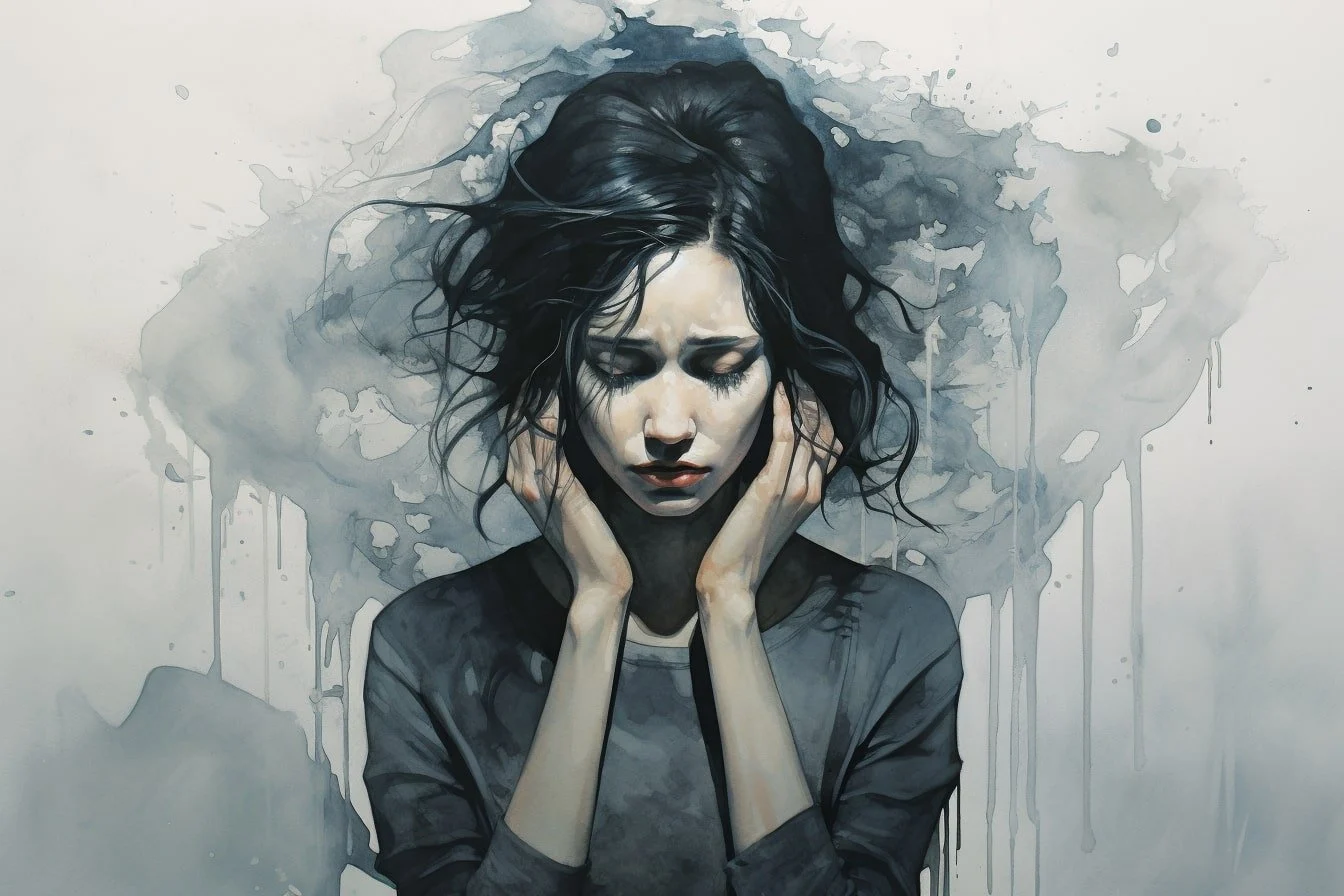
Anxiety and depression are two of the most common mental health disorders affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding these disorders is crucial because they impact not just the individual, but also their families, workplaces, and society as a whole. People with anxiety often experience persistent, excessive worry about various aspects of daily life, and this worry can disrupt their normal activities. Depression, on the other hand, involves persistent feelings of sadness and a lack of interest in activities once enjoyed, affecting how a person thinks, feels, and handles daily activities. Recognizing and addressing these conditions is essential for maintaining overall well-being.
Anxiety disorders come in various forms, including Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Panic Disorder, Social Anxiety Disorder, and specific phobias. GAD involves excessive, uncontrollable worry about everyday matters, while Panic Disorder is characterized by sudden and repeated attacks of intense fear, often accompanied by physical symptoms like heart palpitations and dizziness. Social Anxiety Disorder involves an intense fear of social situations, where individuals worry about being judged or embarrassed in front of others. Specific phobias involve an irrational fear of specific objects or situations, leading to avoidance behavior. These disorders can significantly interfere with daily life, making it important to understand their symptoms and seek appropriate treatment.
The symptoms of anxiety can be both physical and emotional. Physically, anxiety can cause increased heart rate, sweating, trembling, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can be frightening and often mimic those of more serious medical conditions. Emotionally, anxiety can lead to feelings of dread, irritability, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating. These emotional responses can significantly affect daily functioning, making it challenging to focus on work, school, or personal relationships. Recognizing these symptoms and understanding their impact is the first step toward seeking help and managing anxiety effectively.
Depression also manifests in various forms, including Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia), Bipolar Disorder, and Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD). MDD is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and a lack of interest in activities, while Dysthymia involves a chronic form of depression with a depressed mood for most of the day, more days than not, for at least two years. Bipolar Disorder involves episodes of mood swings ranging from depressive lows to manic highs, affecting energy levels, behavior, and the ability to think clearly. SAD is a type of depression that occurs at a specific time of year, usually in the winter when there is less natural sunlight. Understanding these different forms of depression helps in recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
The symptoms of depression can be both physical and emotional. Physically, depression can cause changes in appetite and weight, sleep disturbances, fatigue, and unexplained aches or pains. Emotionally, depression involves persistent sadness, hopelessness, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, and a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed. These symptoms can significantly impact daily life, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks and enjoy life. Recognizing these symptoms and understanding their impact is crucial for seeking help and managing depression effectively.
The causes of anxiety and depression are multifaceted, involving biological, environmental, and psychological factors. Biologically, genetics can play a significant role, with chemical imbalances in the brain, such as low levels of serotonin, being linked to these disorders. Environmentally, stressful life events, such as the loss of a loved one, financial problems, or trauma, can trigger anxiety and depression. Long-term exposure to stress can also be a factor. Psychologically, personal traits like perfectionism, low self-esteem, and a tendency to be overly critical of oneself can contribute to the development of these disorders. Understanding the various causes of anxiety and depression helps in identifying potential risk factors and seeking appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing anxiety and depression involves both self-assessment and professional evaluation. Self-assessment tools, such as questionnaires and online tests, can help individuals recognize symptoms of anxiety and depression. However, these should not replace professional evaluation. A mental health professional can provide a thorough evaluation, including a detailed interview and possibly psychological testing, to diagnose anxiety and depression accurately. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for effective treatment and management of these disorders.
Treatment options for anxiety and depression include medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Medications such as antidepressants and benzodiazepines can help manage anxiety symptoms, while antidepressants are commonly prescribed to treat depression. These medications can take several weeks to start working, and it may take some time to find the right one. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and other forms of psychotherapy are effective in treating both anxiety and depression. These therapies help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and develop coping strategies. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate sleep, can significantly reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. Avoiding caffeine and alcohol can also help. Incorporating these changes into daily life can improve overall well-being and help manage symptoms.
Medications for anxiety and depression include antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are common antidepressants used to treat both anxiety and depression. Benzodiazepines and beta-blockers can help with acute anxiety symptoms, but these medications are usually prescribed for short-term use due to the risk of dependency. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage for each individual.
Therapies for anxiety and depression include Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and psychotherapy. CBT focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors, making it effective for both anxiety and depression. This therapy can be done individually or in group settings, providing flexibility in treatment options. Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, involves discussing thoughts, feelings, and behaviors with a therapist. It helps individuals understand their mental health conditions and develop coping strategies. Both CBT and psychotherapy are valuable tools in managing anxiety and depression, providing long-term benefits and improving overall mental health.
Lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing anxiety and depression. Regular physical activity, such as walking, running, or yoga, can help reduce symptoms by releasing endorphins and improving overall well-being. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports mental health, while avoiding processed foods and sugary snacks is important. Getting enough quality sleep is crucial, and establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a restful environment can help improve sleep patterns. These lifestyle changes, along with medication and therapy, can help manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
Coping strategies for anxiety and depression include mindfulness, meditation, and stress management techniques. Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help individuals stay grounded and reduce symptoms. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and journaling can help manage stress and improve mental health. Developing a strong support system of family and friends can provide emotional support and encouragement during difficult times. Joining support groups allows individuals to share their experiences and learn from others who are going through similar challenges. These coping strategies can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Anxiety and depression are the first steps toward managing these disorders. It’s important to seek professional help and explore various treatment options to find what works best for you. Remember, you are not alone, and with the right support and resources, it is possible to live a fulfilling life. Whether through medication, therapy, lifestyle changes, or support systems, there are many ways to manage and overcome anxiety and depression. Don’t hesitate to reach out for help and take the first step towards a healthier, happier future.